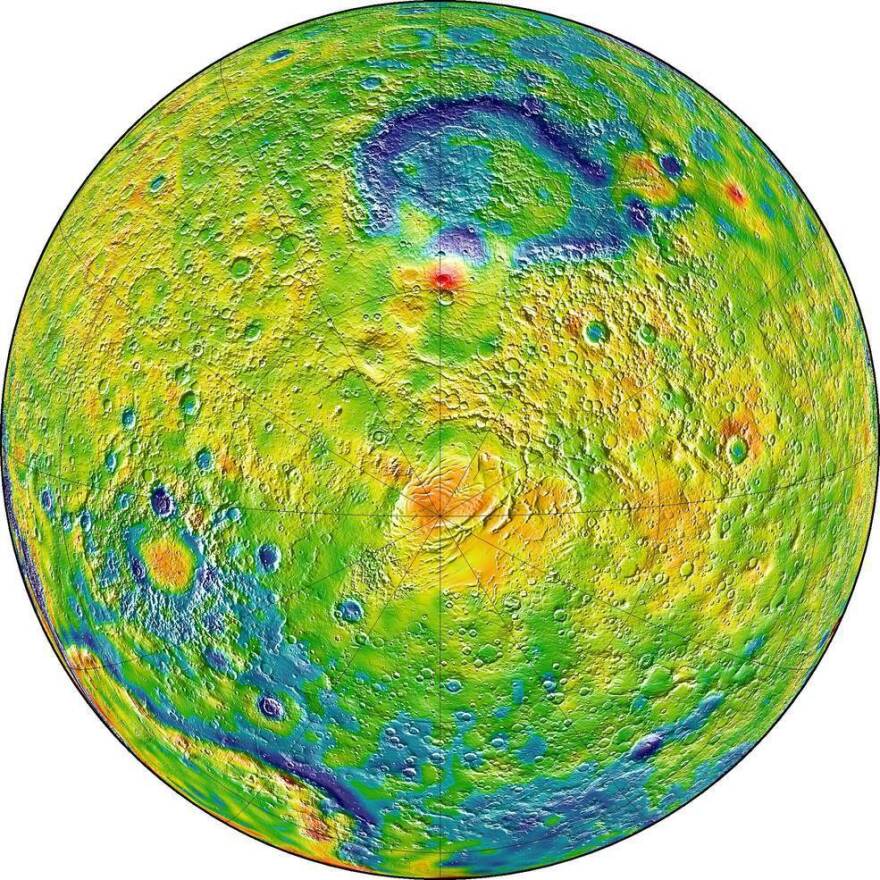
NASA has released a new gravity map of Mars, providing a detailed look at the Red Planet's surface and revealing new information about what lies beneath it.
The map was made by tracking subtle variations in the planet's gravitational pull on orbiting spacecraft. As NASA explains: "The pull will be a bit stronger over a mountain, and slightly weaker over a canyon."
Using this technology, it's possible to look inside a planet "just as a doctor uses an X-ray to see inside a patient," Antonio Genova of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, who was lead author of a paper on Mars' gravity, said in a NASA press release.
And the NASA release says this improved view confirms that "Mars has a liquid outer core of molten rock." The researchers determined this by "analyzing tides in the Martian crust and mantle caused by the gravitational pull of the sun and the two moons over Mars."
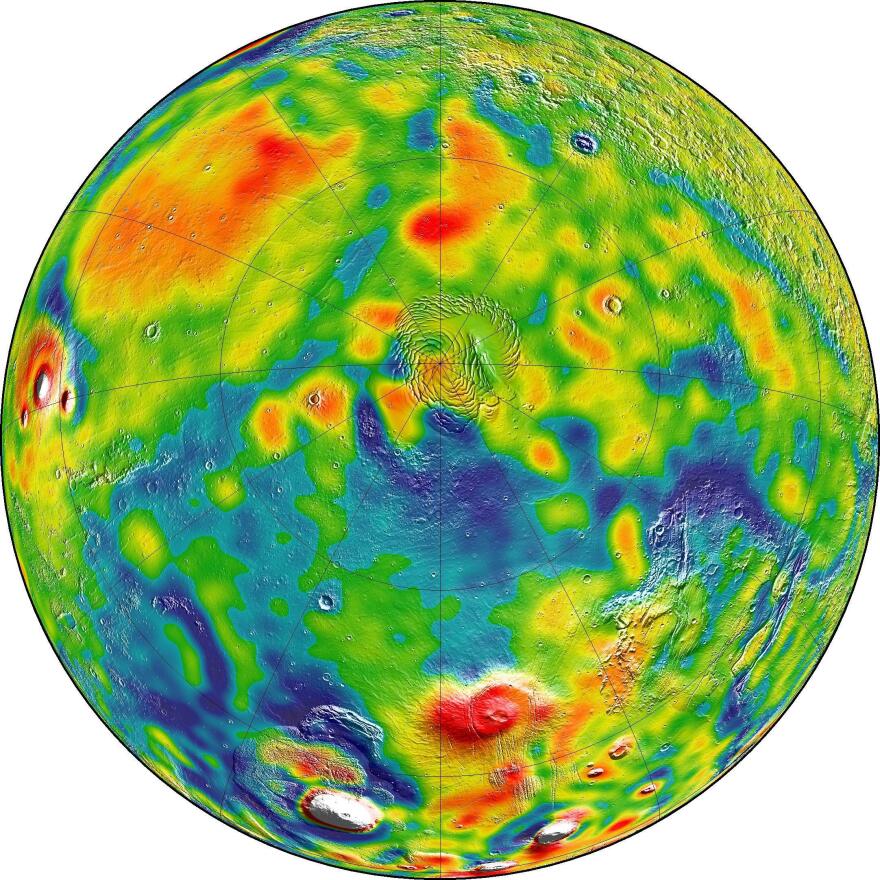
The map also provides new details about the Red Planet's ice caps. NASA says it was able to use data from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to determine "that when one hemisphere experiences winter, approximately 3 to 4 trillion tons of carbon dioxide freezes out of the atmosphere onto the northern and southern polar caps, respectively."
Scientists say the more detailed knowledge of Mars' surface and gravitational dynamics will also assist in future missions to the planet's orbit.
Copyright 2020 NPR. To see more, visit https://www.npr.org.