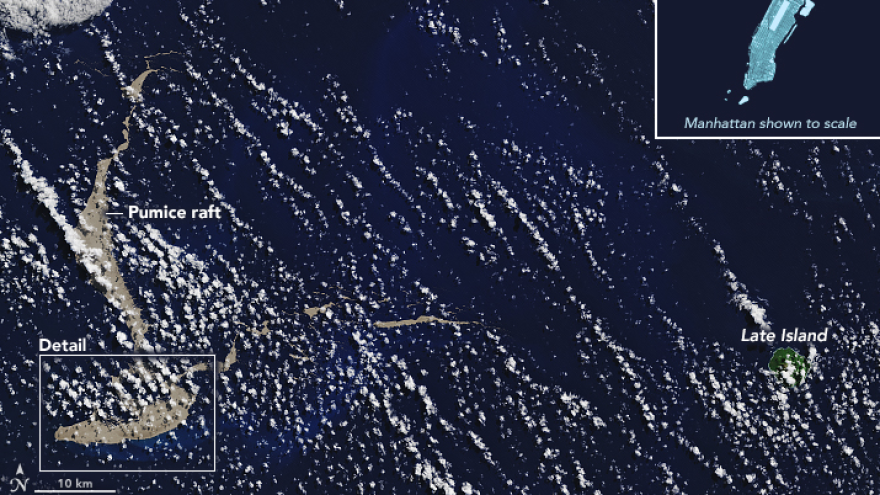
A massive raft made of pumice stones is floating toward Australia, carrying marine organisms that scientists say could help replenish Australia's Great Barrier Reef.
Some of the stones are as large as basketballs and have formed a giant sheet stretching about 58 square miles — nearly the size of Washington, D.C.
An explosion from an underwater volcano near the tiny island nation of Tonga is thought to have produced the raft, according to NASA.
Michael Hoult and Larissa Brill, an Australian couple sailing to Fiji on a catamaran, posted to Facebook about the pumice sheet on Aug. 17.
They had heard the previous day of "pumice fields," and in a Facebook post, they reported they encountered a "faint but distinct smell of sulfur" when they were near a location "charted as area of volcanic activity."
Later, the couple wrote they "entered a total rock rubble slick made up of pumice stones from marble to basketball size ... The rubble slick went as far as we could see in the moonlight and with our spotlight."
Volcanoes have "a lot of dramatic ways to announce their presence," according to NASA, including plumes of ash and steam, lakes of lava, mud flows and earthquakes, and the sudden rising of an island above a water's surface.
"One of the more subtle and rarely observed displays is the pumice raft," according to NASA. "Many of the world's volcanoes are shrouded by the waters of the oceans. When they erupt, they can discolor the ocean surface with gases and debris. They also can spew masses of lava that are lighter than water. Such pumice rocks are full of holes and cavities, and they easily float."
Scott Bryan, an associate professor at Queensland University of Technology, told the Australian Broadcasting Corp. that the raft is floating toward Australia and will hit the coast in about seven to 12 months. He says by that time, the raft will be "covered in a whole range of organisms of algae and barnacles and corals and crabs and snails and worms."
"Each piece of pumice is a rafting vehicle. It's a home and a vehicle for marine organisms to attach and hitch a ride across the deep ocean to get to Australia," Bryan told The Guardian.
Bryan said the organisms will help regenerate the Great Barrier Reef's corals, half of which have been destroyed by climate change.
Copyright 2020 NPR. To see more, visit https://www.npr.org.
A raft of rock, the size of 20,000 football fields is floating towards Queensland. The pumice was created when an underwater volcano erupted off Tonga. Scientists say it'll bring millions of new coral to the Great Barrier Reef. @ErinEdwards7 @QUT #7NEWS pic.twitter.com/W7pKdowYw2
— 7NEWS Gold Coast (@7NewsGoldCoast) August 24, 2019